Nagara Style Temple
The Nagara Style Temple Architecture emerged during the Gupta period. The progression can be traced in the form of 5 stages as follows
Stage 1– In this stage square temple with a flat roof was created. It was created on a grounded platform and had shallow pillars.
Ex- Temple No. 17 of Sanchi
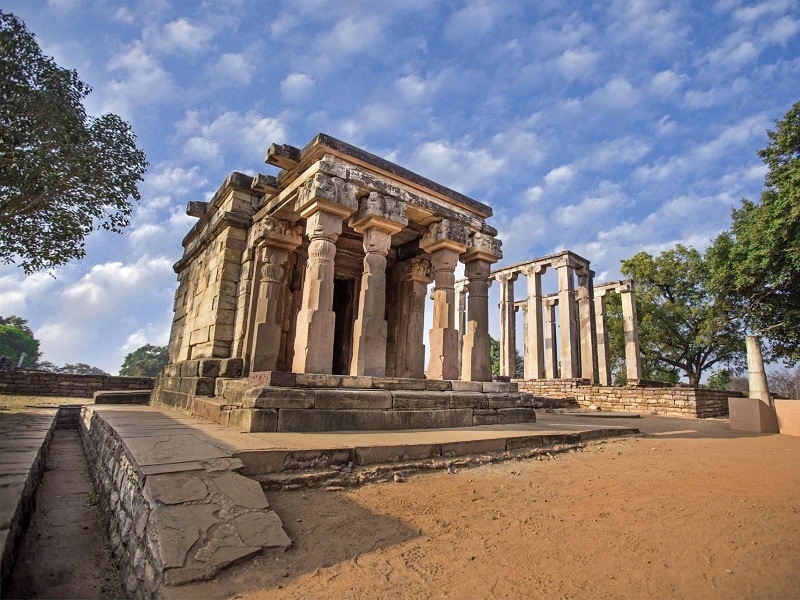

Stage 2– Square temple approach continued with addition of creation on an upraised platform. Pillars were not shallow in nature.
Ex- Parvati temple of Nachna-Kuthara in Madhya Pradesh
-1640863583.jpg)
Stage 3– In addition to features of previous stage, it had curvilinear tower known as Sikhara. This stage is considered as precursor of Nagara style of temple.
Ex- Dashavatar temple of deogarh, Jhansi

Stage 4– In this stage the main shrine became more rectangular in shape.
Ex- Ter temple in Maharashtra
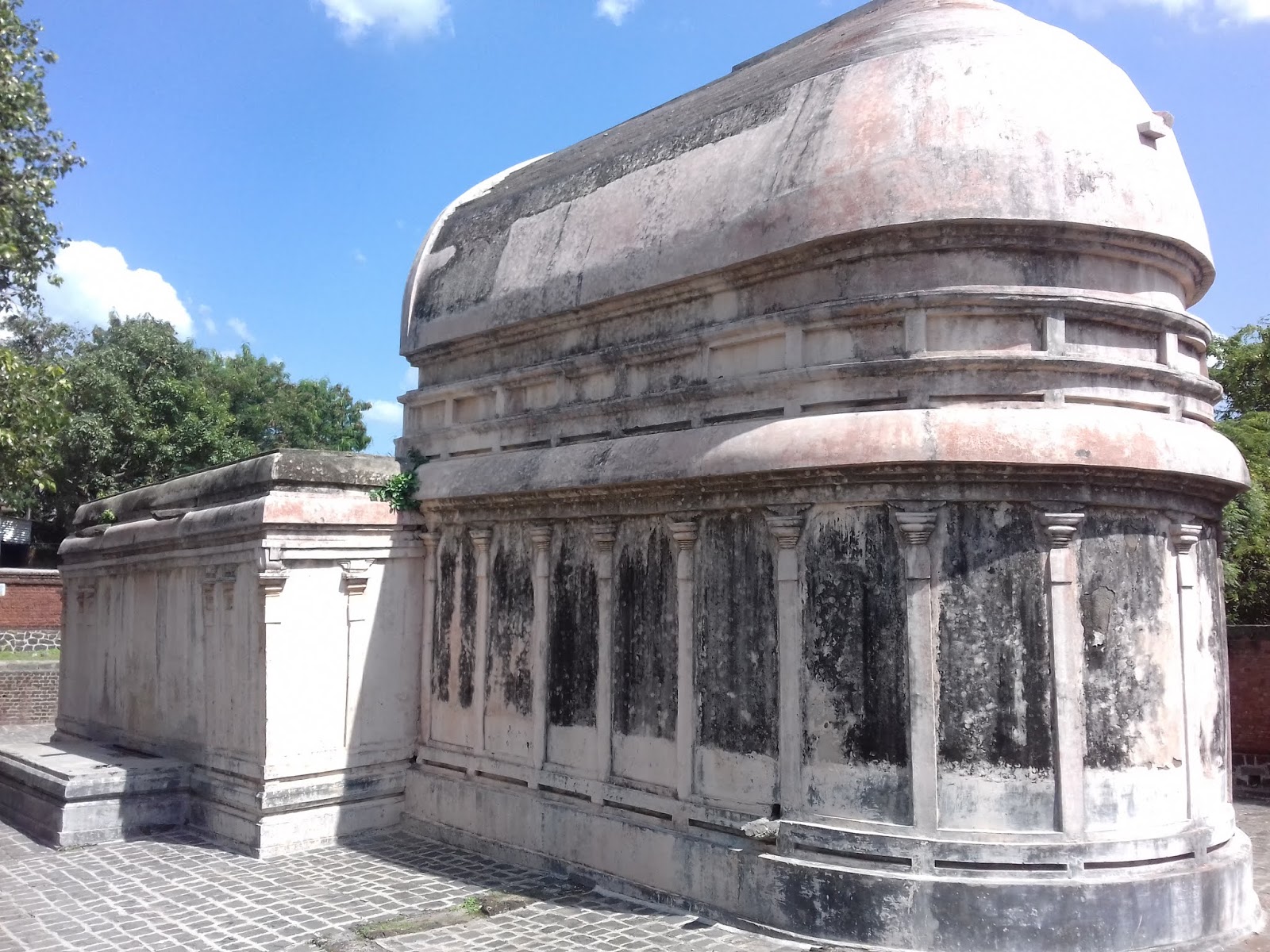

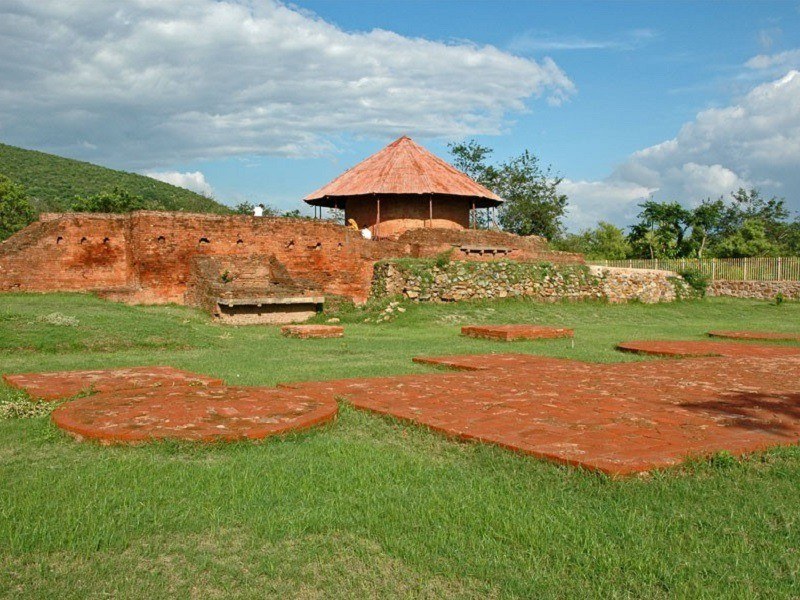
Stage 5– In this stage, circular temples with shallow rectangular projections were introduced.
Ex- Maniyar Math at Rajgir

Features of Nagara Style Temple
- The characteristic feature of nagar style temple is curvilinear tower known as Rekha prashad Shikhar.
- Shikhara is paused by amalak and the top most part of shikhara is finial(which is generally an weapon carried by the temple God)
- Mandap is the big gallery where prayers are offered and performance of religious rituals also take place. Mandap is also supported by pillars.
- Garbha griha is the most sacred place of the temple. It is also called sanctum sanctorum.
- Temples do not have a boundary wall in this style of temple architecture.
- Water tanks are also absent here because of the presence of rivers or other water bodies.
- Outside the Garbhagriha, images of the river goddesses Ganga and Yamuna and Mithun were placed.
- It follows crucified ground plan.
- The vertical end of the shikhara ended in a horizontal fluted disc, known as the Amalak.
- On top of that, a spherical shape was placed known as the Kalash.
- The ambulatory passageway or the pradakshina path around the sanctum sanctorum was covered.
Substyles of Nagara School of Architecture
Odisha Style of Temple
In different parts of the Kalinga empire, this distinct style of temple architecture developed. This style was developed by ganga dynasty and gajapati dynasty
Some of its features were:
The characteristic feature of Orissa temple is presence of deula shikhara which is mostly vertical till top and suddenly starts curving near top.
The exterior walls were lavishly decorated with intricate carvings, but interior walls were kept plain.
There was no use of pillars in the porch. Iron girders were used instead to support the roof.
The mandap was known as jagamohan in this region.
Temples were surrounded by a boundary wall as in Dravidian style of temple architecture.

Khajuraho School
This style was developed by chandela rulers of Bundelkhand.
Some of the features are
-The chambers in temples were interconnected in East West direction.
-They were made of sandstones
-One of the characteristic features is the presence of multiple shikhar and half Shikhar known as Urushringa.
-Both exterior and interior walls of the temple were lavishly decorated with intricate carvings.
-The carvings included erotic images or sexual coitus as well.
-The images of the walls of temples depict concept of Dharma, Artha, Kamma, and Moksha
-Not only Hindu but Jain Temples were also created in this style.
Ex – Kandaria Mahadev Temple
Lakshman Temple
Parsvnath Temple
Vishwanath Temple

Solanki School
These temples were developed by solanki rulers (Solankis are clans of chalukya) of Gujarat.
Some of the features include
-Exterior walls are optimally decorated while interior walls are decorated with intricate carvings.
-Temples were generally east facing because it was believed that on the day of equinox, sun directly illuminates the shrine.
– A unique feature of this school is the presence of step tank, known as Suryakund in the proximity of the temple.
-The marble carvings of this style highly resembles the excellence of wooden carpentry.
Ex- Somnath temple, Kathiawar
Sun Temple, Modhera
Dilwara Jain Temple, Mount Abu
You May also Like:
How to Choose UPSC Optional Subjects?
All About UPSC CSE 2024




Pingback: Dravidian style temple Architechture| Dravida Temple- Eduexa
Pingback: Folk Dances of India | Folk Dances for UPSC, SSC - Eduexa