Indo Pak Relations
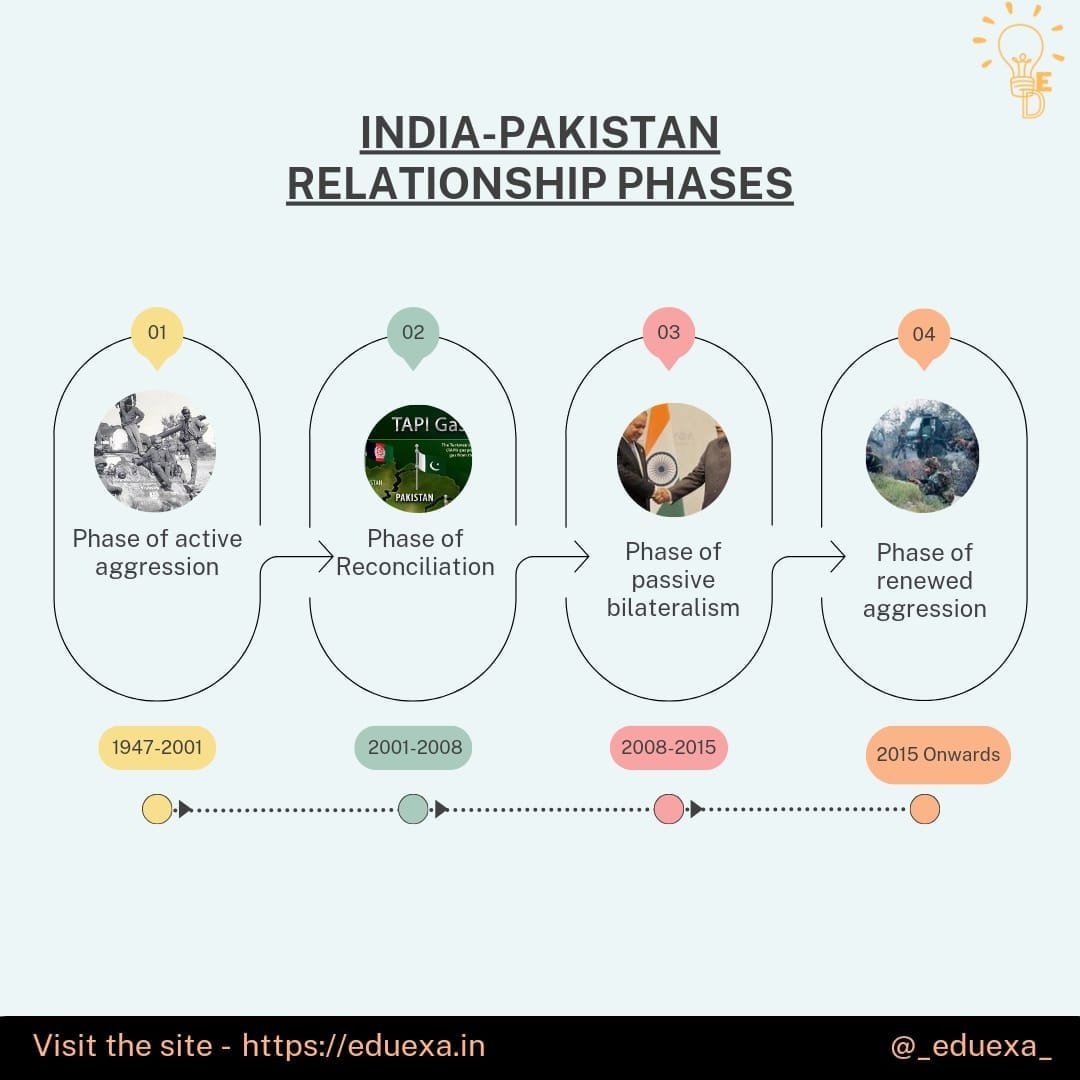
Phase of Active Aggression (1947-2001)
1947- 1st Indo Pak War
It resulted in the ceasefire line being demarcated.
UN intervention was allowed to begin negotiation.
1/3rd of Jammu and Kashmir was being occupied by Pakistan (Gilgit Baltistan area)
1965-2nd Indo Pak War (Second Kashmir War)
It was the result of a series of skirmishes between India and Pakistan between April 1965 and September 1965. It started with “Operation Gibraltar” by Pakistan, which was planned to penetrate and conquer Jammu and Kashmir.
In the Rann of Kutch, a desolate region in the Indian state of Gujarat, war broke out between India and Pakistan.
After the US and the Soviet Union began peace negotiations, the Tashkent Declaration, a peace treaty, was signed by India and Pakistan in January 1966 with help of UN. Under the treaty, both sides agreed to return occupied territories, withdraw troops, and return to the boundaries defined in 1949. Hajipir was also
1971-3rd Indo Pak War (Shimla Agreement 1972)
It demarcated the line of control between India and Pakistan. Demarcation was not made beyond NJ9842 i.e Siachen glacier was left out of boundary demarcation.
Along with it, the Shimla Agreement also accepted release of around 96000 prisoners of war by Indian authorities.
1984-Operation Meghdoot
It was the codename for the Indian Armed Forces’ operation to seize control of the Siachen Glacier in the then state of Jammu and Kashmir (now in Ladakh), precipitating the Siachen conflict.
1980’s and 1990’s- Insurgency in Kashmir
Kashmir area continued to witness insurgency and terrorist activities during this period. Anti Indian sentiments were on the rise among the people.
1998- Both India and Pakistan entered Nuclear Club
1999- Kargil war
The Kargil War began when members of the Pakistan military infiltrated the region around Kargil, hoping to be able to gain control of the town due to its strategic placement. Indian army conducted “Operation Vijay” as it’s response and led to India’s victory.
2001-Attack on Indian Parliament
Five terrorists from Lashkar-e-taiba attacked Parliament House in which nine security personnel lost their lives.
2) Phase of Reconciliation (2001-2008)
1999-Lahore declaration
Delhi Lahore bus service were started as a confidence building measure
Vajpayee’s principle of Insaniyat (humanism), Jamhooriyat (democracy) and Kashmiriyat (Kashmir’s legacy).
2008-TAPI gas pipeline project
It is 1,814km natural gas pipeline that originates from Turkmenistan and passes through Afghanistan and Pakistan to reach India. It acts as an energy bridge between Central Asia and South Asia.
2008-Mumbai attack
It refers to series of attack which took place in November, when 10 members of Lashkar-e-taiba militant group carried out 12 coordinated shooting and bombing attacks across Mumbai which led to massive killings. With the deadly Mumbai attack of 26/11 reconciliation phase came to an end.
3) Phase of Passive Bilateralism (2008-2015)
2014-Neighbourhood 1″ policy
This policy accorded higher priority to India’s immediate neighbours in South Asia for bilateral ties and cooperation.
Gujaral Doctrine
It believes in maintaining friendly relations with neighbours by giving line of credits, aids with no reciprocity, soft diplomacy etc.
4) Phase of renewed Aggression ( From 2015)
2015- CPEC
It is a bilateral project between Pakistan and China, intended to promote connectivity across Pakistan with a network of highways, railways, and pipelines accompanied by energy, industrial, and other infrastructure development projects.
2015-Gurdaspur terror attack
2016-Pathankot attack, Uri attack
Seven IAF personnel were killed when four JeM terrorists sneaked into the Pathankot Air Force Station on 2 January 2016. The siege went on for three days.
2017-Amarnath Yatra attack
Terrorists attack by LeT group which led to killing of 7 yatris.
2019-Pulwama attack
It occurred on 14 February 2019, when a convoy of vehicles carrying Indian security personnel on the Jammu–Srinagar National Highway was attacked by a vehicle-borne suicide bomber at Lethapora in the Pulwama district of the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir. It resulted in India-Pakistan military standoff.
Oct 2019-Abrogation of Article 370
On August 6, 2019, the Government of India revoked the special status, or autonomy, granted under Article 370 of the Indian Constitution to Jammu and Kashmir. Consequently, Jammu and Kashmir state was divided into 2 union territories as Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.
It is believed that with the abrogation of article 370 which was repeatedly used by Pakistan to create insurgencies and chaos in Kashmir can be better put at halt.
Read a complete Guide on How to Choose UPSC Optional Subjects


Pingback: What is Diplomacy|Types of Diplomacy- Complete Guide in 2024