ST full form is Scheduled Tribes. These are the tribal or indigenous communities who have been designated or referred as “Scheduled Tribes” by the government of India. ST/SC/OBC/EWS are group of people who comes under the reserved category and the process of identification of each of these groups has been mentioned in the constitution for upliftment and progression of ST, SC, OBC and EWS. This detailed blog will discuss everything related to Scheduled tribe including ST full form, meaning, constitutional identification, certificate application as well as the benefits of ST.
What are Scheduled Tribes?
ST full form is Scheduled Tribe who are also commonly referred as Adivasis or indigenous peoples. These are simply the communities that have been designated as “Scheduled Tribes” by the government of India. These communities are primarily considered as primitive and often reside in forests. They are cut off from mainstream society and live in their own way. Because of being disconnected from the main society and advantages, they are entitled to certain protections and benefits under the Indian Constitution.
Scheduled Tribes are spread across different states in India and have their own distinct cultures, languages, and traditions. They often face challenges such as poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and discrimination. The government of India has implemented various programs and policies to address these issues and promote the socio-economic development of Scheduled Tribes.
Concept of Caste System in India
Indian Caste system is around thousands of years old which is a complex social hierarchy system, in which society divided into groups (castes or categories) based on their occupation, birth etc. It’s still prevalent in India with the main 4 Category or Caste System that are as follows:
- General Category (UR Category)
- OBC (Other Backward Classes)
- SC (Schedule Caste)
- ST (Schedule Tribe)
- EWS (Economically Weaker Sections)
ST Full Form in Hindi
The full form of ST in hindi is “अनुसूचित जनजाति“.
The term “Scheduled Tribes” comes from the Constitution of India, which lists certain tribal communities as being eligible for special treatment and protection under the law. These communities are referred to as “Scheduled Tribes” and are also known as “Adivasis” or “Indigenous Peoples.”
Implementation and Designation of Scheduled Tribe
Article 366 (25)
Article 366 (25) of the Constitution of India defines the Scheduled Tribes as “Such tribes or tribal communities or part of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under Article 342 to the Scheduled Tribes for the purposes of this [Indian] Constitution”.
Article 342
(1) The President may with respect to any State or Union Territory and where it is a State, after consultation with the Governor thereof by public notification, specify the tribes or tribal communities or parts of or groups within tribes or tribal communities which shall for the purpose of this Constitution be deemed to be Scheduled Tribes in relation to that State or Union Territory, as the case may be.
(2) Parliament may by law include in or exclude from the list of Scheduled Tribes specified in a notification issued under clause any tribe or tribal community or part of or group within any tribe or tribal community, but save as aforesaid a notification issued under the said clause shall not be varied by any subsequent notification.
Scheduled Tribes (STs) are identified based on indications of primitive traits, distinctive culture, geographical isolation, shyness of contact with the larger community, and overall backwardness.
History of ST (Scheduled Tribes)
Do you think reservation or ST categorisation was just any political move? No, it has a long history of discrimination, oppression, and marginalization. The ST or tribal communities in India have faced social and economic discrimination for centuries, and have often been treated as outcasts by the dominant castes in Indian society.
The STs are a diverse group of communities, each with its own distinct culture, language, and traditions. They are spread across the country and are found in almost every state and union territory in India. Many STs live in rural areas and engage in traditional occupations such as farming, forestry, and hunting and gathering.
In modern times, the Indian Constitution has recognized the STs as a distinct social group and has taken steps to address the historical discrimination and marginalization that they have faced. These steps include affirmative action programs such as reservation in education and employment, and the implementation of laws to protect the rights and dignity of STs.
“Check out the upcoming government exams in 2025″
Benefits of ST (Scheduled Tribes)
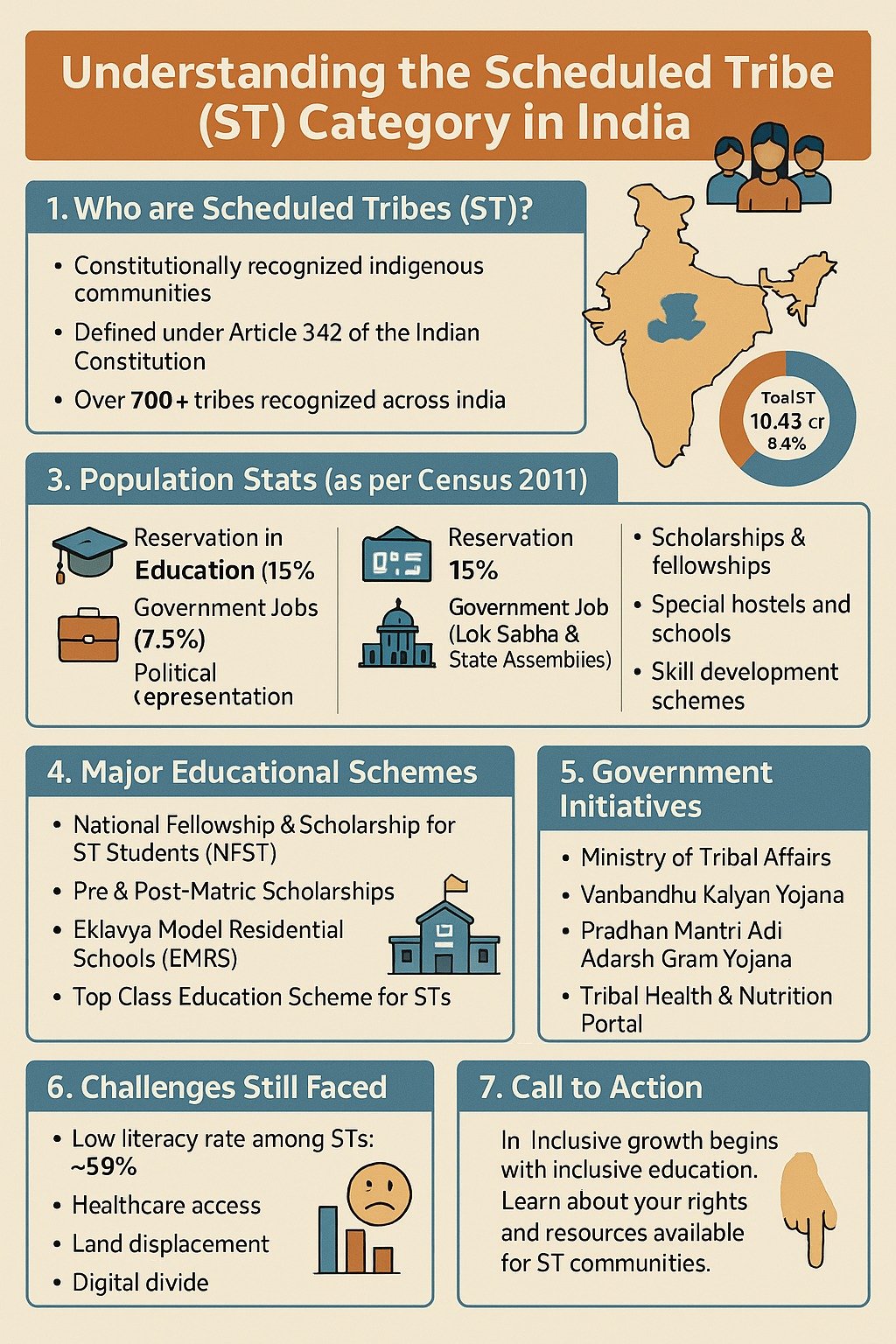
In India, Scheduled Tribes (STs) are socially and educationally disadvantaged groups that have been historically subjected to discrimination and oppression. The Indian Constitution provides for affirmative action measures to uplift these groups and ensure their inclusion and equality in society.
- One of the major benefits that people with ST category certificates receive is reservation of seats in educational institutions and government jobs. A certain proportion of seats are reserved for ST category that means these seats or vacancies can only be filled by the candidates under this category. As a results, they benefit by lower cut-offs at any stage of examination. The purpose of this measure is to ensure that STs have equal opportunities to access education and employment, and to help address the historical disadvantage faced by these groups.
- Not only the reservation of seats and jobs, STs are also eligible for various other benefits and schemes aimed at improving their socio-economic status. These benefits may vary ranging from financial assistance for education to subsidies for starting businesses to access to credit at lower interest rates.
- STs living in remote and tribal areas may also be eligible for special schemes and benefits aimed at improving their access to basic amenities such as healthcare, education, and clean drinking water.
National Commission for Scheduled Tribe
The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST) is a statutory body in India that was established under the provisions of the Constitution (89th Amendment) Act, 2003. This commission (i.e. NCST) is responsible for the protection, welfare, and development of Scheduled Tribes and it also takes possible actions and inquiry into any matter regarding deprivation of rights of the ST.
The NCST has a number of powers and functions to perform as discussed in the following section:
- To investigate and monitor all matters relating to the safeguards provided for Scheduled Tribes under the Constitution or any other law.
- To inquire into specific complaints regarding the deprivation of rights and safeguards of Scheduled Tribes.
- To participate and advise on the planning process of socio-economic development of Scheduled Tribes and to evaluate the progress of their development under the Union and any State.
- To present the reports about the working of those safeguards the President, annually and at such other times as the Commission may deem fit.
- To make recommendations for the effective implementation of those safeguards and other measures for the protection, welfare, and socio-economic development of Scheduled Tribes.
The NCST is headquartered in New Delhi and has regional offices in various states of India. It is composed of a Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson, and five other Members, all of whom are appointed by the President of India. The NCST operates under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and works closely with other government agencies and non-governmental organizations to promote the welfare and development of Scheduled Tribes in India.
Documents Required to Get SC ST OBC Certificate
If you also fall under this category and still haven’t applied for the caste or category certificate it is important that you get your certificate for getting reservation benefits. If you are wondering what all documents are required to get EWS/SC/ST/OBC certificate To get an SC (Scheduled Caste), ST (Scheduled Tribe), or OBC (Other Backward Class) certificate in India, you will generally need to provide the following documents:
- Proof of identity: This could be a passport, PAN card, voter ID, or any other government-issued identification that has your photo, name, and address.
- Proof of residence: This could be a utility bill, rent agreement, or any other document that shows your current address.
- Birth certificate: This is required to prove your age and place of birth.
- Proof of caste: This could be a caste certificate issued by a competent authority, or a certificate issued by a previous employer, educational institution, or government agency that confirms your caste.
- Affidavit: You may need to provide an affidavit stating that you belong to the SC, ST, or OBC category and that you have not availed the benefits of reservation under this category before.
Note that the specific documents required may vary depending on the state in which you are applying for the certificate and the category for which you are applying. It is best to check with the local authorities or the office responsible for issuing SC, ST, or OBC certificates for the exact requirements.
Difference Between SC and ST
While both the categories are reserved categories, they are not the similar categories. SC and ST are abbreviations for Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe, respectively. These are official terms used in the Indian Constitution to refer to certain historically disadvantaged social groups.
| SC | ST | |
| Full form | SC Full form is Scheduled Caste | ST full form is Scheduled Tribe |
| Meaning | The Scheduled Castes are a group of communities or castes which are considered as being socially and economically disadvantaged because of historical designation as outcastes from the Hindu caste system. | The Scheduled Tribes are indigenous communities that have a distinctive culture, language, and way of life. |
| Classification | SC or Scheduled Castes are considered to be a part of the Hindu social system. | Whereas ST are considered to be distinct indigenous communities with their own cultural and social practices. |
| Articles | Article 366 (24) of the Constitution of India defines the Scheduled Castes as: Such castes, races or tribes or part of or groups within such castes, races or tribes as are deemed under Article 341 to be Scheduled Castes for the purpose of this [Indian] constitution. | Article 366 (25) of the Constitution of India defines the Scheduled Tribes as “Such tribes or tribal communities or part of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under Article 342 to the Scheduled Tribes for the purposes of this [Indian] Constitution”. |
Reservation System in India

In India, there are various types of reservation systems in place for various purposes. Here are some examples:
- Educational institutions: Many educational institutions in India like Delhi University etc. have a reservation system for admissions where the cut offs for each category differs. This reservation is based on factors such as caste, religion, and nationality.
- Government jobs: Another place where reservations exist is the government jobs. Almost every government exam like those conducted by UPSC, SSC etc have different relaxations for people belonging to SC, ST, OBC and EWS. This reservation is based on factors such as caste, religion, and nationality.
- Political representation: The Indian constitution provides for reservation of seats in the parliament and state legislative assemblies for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs). This reservation is aimed at providing representation to these historically disadvantaged groups. Further, Nari Shakti vandan Act 2024 has provided for reservations for women in Lok sabha and state assemblies.
- Public transportation: Some states in India have a reservation system for certain categories of passengers on public transportation, such as buses and trains. This reservation is based on factors such as age, disability, and military service.
- Housing: Some states in India have a reservation system for housing, which provides certain categories of people with priority in the allocation of government-owned housing.
Overall, the reservation systems in India are meant to address historical imbalances and ensure that certain groups have equal opportunities in various fields. However, there has been much debate and controversy surrounding these systems, with some people arguing that they are necessary to address historical injustices and others arguing that they are unfair and create divisions within society.
List of Scheduled Tribes
Scheduled tribes are groups of people who have been formally recognized by the government of India as being socially and economically disadvantaged and in need of special protection and support. There are a total of 705 scheduled tribes in India. Here is a list of some of the major scheduled tribes in India:
- Adivasis: This is a broad term used to refer to indigenous communities in India. Adivasis are found in many states of India, including Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, and Odisha.
- Bhils: This is a large tribal group found in the states of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra.
- Gonds: This is a tribal group found in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Santhals: This is a tribal group found in the states of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, and Bihar.
- Mundas: This is a tribal group found in the states of Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal.
- Oraons: This is a tribal group found in the states of Jharkhand and Odisha.
- Kondhs: This is a tribal group found in the states of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
This is just a small sampling of the scheduled tribes in India. There are many other tribal groups found in different parts of the country, each with its own unique culture, language, and traditions.
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide has covered all the sections related to Scheduled Tribes starting from ST full form to historical perspective to present day benefits. Further the classification and difference between SC and ST has been elaborated for better clarity. Now that you have understood about the category and certificate application, it is essential to get the certificate to claim the reservation.
FAQs
1. What is ST full form?
ST full form in English is scheduled tribes whereas in Hindi it is “अनुसूचित जनजाति”.
2. What is meant by ST caste?
ST category stands for the communities that are indigenous tribes of India which are considered primitive and distant from the mainstream.
3. Which caste is the ST category?
The castes or communities that are officially designated as “Scheduled Tribe” under article 342 for the purpose of the Indian Constitution are considered as ST.
4. What are SC, ST and OBC?
SC stands for scheduled Castes, ST stands for Scheduled Tribes and OBC stands for Other Backward Class.