Modern Slavery : A Comprehensive Guide in 2024 – Eduexa
MODERN SLAVERY
G20 countries including India are fuelling modern slavery, says new report. G-20 summit has significantly brought modern slavery and its illl effects to the fore.
Recent Context
Walk Free (international human rights group) released the Global Slavery Index 2023, an assessment of modern slavery conditions in 160 countries.
Index uses the data released by International Labour Organisation (ILO), Walk Free, and International Organisation for Migration (IOM).
What is modern slavery?
Modern slavery refers to situations of exploitation that a person cannot refuse or leave because of threats, violence, coercion, or deception.
It is an umbrella term that comprises various instruments of repression in the form of bonded labour, sexual exploitation, women and child trafficking, forced marriages and other.
Key findings
50 million people were living in modern slavery on any given day in 2021, an increase of 10 million people since 2016.
Among the 50 million, 28 million suffer from forced labour and 22 million from forced marriages.
India tops the list with 11 million people working as forced labourers, followed by China, Russia.
North Korea followed by Eritrea has the highest prevalence and Switzerland followed by Norway has the lowest prevalence of modern slavery.
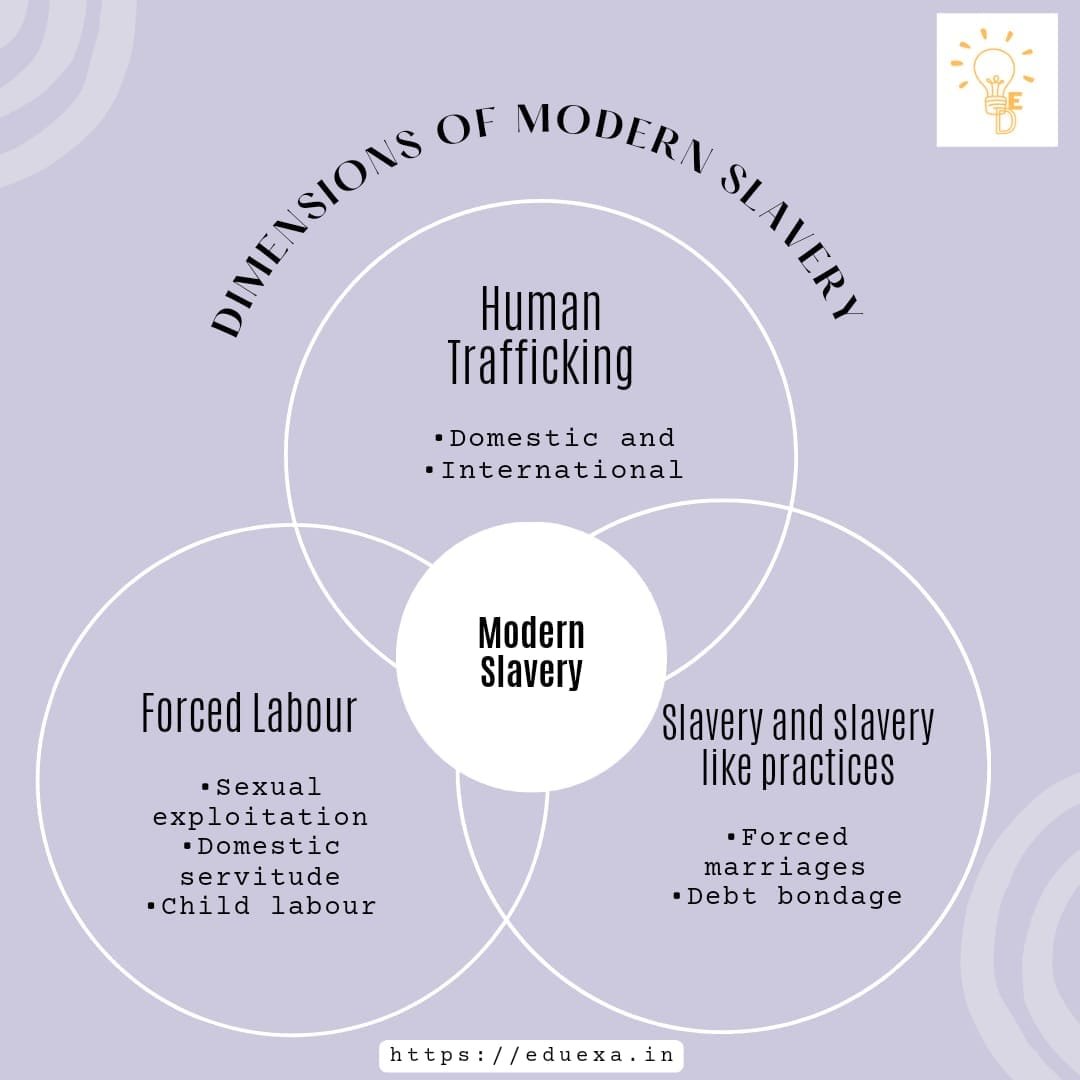
Dimensions of modern slavery
Human Trafficking
- Domestic
- International
Forced labour
- Sexual exploitation
- Domestic servitude
- Worst forms of child labour
Slavery and slavery like practice
- Forced marriages (child marriages)
- Debt bondages
- Child soldiers
Reasons contributing to increased instances of modern slavery
- Climate degradation and natural disasters
- Lower implementation of Human rights
- Gender stereotypes and patriarchy
- COVID-19
- Conflicts both external and internal has an impact of possibility of modern slavery
- Internal emergencies and forced migration
- Minority status in a majoritarian state
- Racial intolerance
- Increased Unemployment
Consequences of Modern Slavery
Human Rights Violation – Higher instances of modern slavery suggest lower enforcement of human rights and empowerment.
Discrimination – Modern Slavery is generally prevalent against the members of a particular caste, class, race or gender.
Gender inequality and reinforced patriarchy– Forced marriages, sexual exploitation and Trafficking of women widens the gender gap and further enforces male domination as women are seen as mere objects in the holds of male members.
Lower standards of living – Modern Slavery includes bonded labour, child labour and other worst forms of atrocities which severely impacts the quality of life of the victims.
Mental Health Disorders – Physical and mental exploitation leaves a long lasting impact on the brain and mental health of the victims.
Sows seeds of further social evils– Modern Slavery can further result in social intolerance and violence and may result in terrorism.
| Modern slavery → Anger and Frustrations → Dissatisfaction from Nation/Government → Terrorism/ Anti-national activities |
Way Forward
Recognise and respond to modern slavery through international cooperation and forums. For example – G-20, UNHRC can be effectively used to address these modern issues.
Formulation of domestic laws- Each country should have a comprehensive law to tackle modern slavery. Each dimension of modern slavery should be covered. For example – India has laws prohibiting Child labour, forced labour, sexual exploitation and child marriages.
Strengthen social protection and safety nets to boost resilience.
Repealing migration policies that place national security above human rights.
Spreading awareness – Individuals need to educate themselves about the issue, demand transparency from companies and report any suspected cases of modern slavery they encounter.
Civil society participation – Non state actors like NGOs, Civil society, pressure groups, etc has an important role to play in not only conducting surveys for reporting instances of modern slavery but also in pushing the government to take required action in this direction.
You may also like:
Difference Between UR Category and EWS Category and how they are different from General Category. Read Here
Read here about the recently head SCO Meeting.

Pingback: Child Marriage in India: Definition, Causes, Impact, Solution- Eduexa